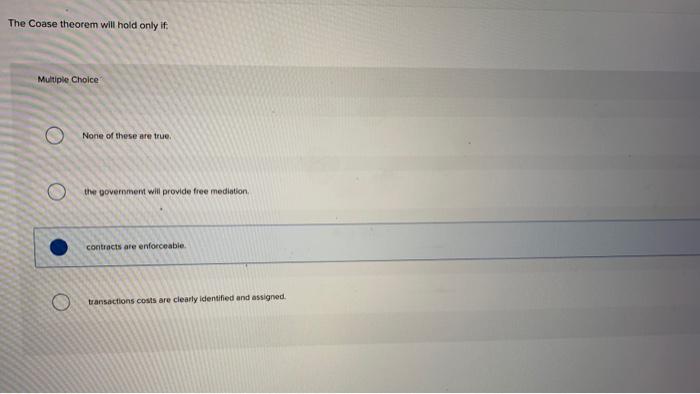
The Coase Theorem Will Hold Only if:
Society would reach the position in which no more costless. We reconsider the well-known BeckerCoase BC theorem according to which changes in divorce law should not affect divorce rates.

Solved 2 The Social Cost Of Cutting Trees For Firewood In A Chegg Com
Thus it is argued the Coase Theorem will only hold in the presence of non-transferable resources giving rise to Ricardian rents Wellisz 1964 p.
. There are no transactions costs. The Coase theorem will hold only if. When negative externalities exist in a market it the producers are forced to pay a pigovian tax then.
People can make enforceable agreements. Y game is empty. Solved The Coase theorem will hold only if.
The Coase theorem will hold only if. Up to 10 cash back Hence when there are three parties instability problems will cause the Coase Theorem to fail if and only if the core of the corresponding three-player majority game is empty. O Neither of these must hold true.
The so-called theorem goes something like this. For the BeckerCoase theorem to hold in this setting utility must be transferable both within marriage and upon divorce and the marginal. Economics questions and answers.
Externalities and the Coase Theorem The Coase Theorem has been one of the most in uential contributions to come from economics in the last fty years. As Calabresi did that the Coase Theorem must hold in the long run we must conclude that if the Coase Theorem is to hold there can be no long run. It can hold only if time stands still.
Its in uence on the law has been especially profound. For instance the farmer would have to find fishers downstream in order to bargain with them. The sellers will bear a greater tax incidence than the buyers.
If transaction costs truly are zero then only a very small subset of desirable transactions will take place. The Coase Theorem named after the British economist Ronald Coase is a famous theorem that addresses the question of how effectively private markets can deal with externalities. The Coase Theorem is a legal and economic theory developed by economist Ronald Coase regarding property rights which states that where there are complete competitive markets with no transaction.
Coase Theorem Assumptions. Indeed while several contributions argue that the Coase theorem may fail to hold most if not all emphasize various forms of inefficiencies such as large transaction costs non-cooperative behavior Aivazian and Callen Reference Aivazian and Callen 1981. The Coase Theorem also holds that in the absence of transaction costs the rights would be efficiently allocated.
Both of these must hold true. We show that the standard Coasean bargaining game involving three parties is strategically equivalent to an asymmetric three player majority game. There are no transactions costs.
Reference Fella Mariotti and Manzini 2004 market failures in the market. Both of these must hold true. The reason is that it can be too tempting to free-ride on others agreements since those others cannot credibly threaten to behave inefficiently upon such strategic non-participation.
Multiple Choice O there are no transactions costs. People can make enforceable agreements. We use this equivalence result to derive all instances in which the Coase Theorem will and will not hold with three parties and show that a priori such instability.
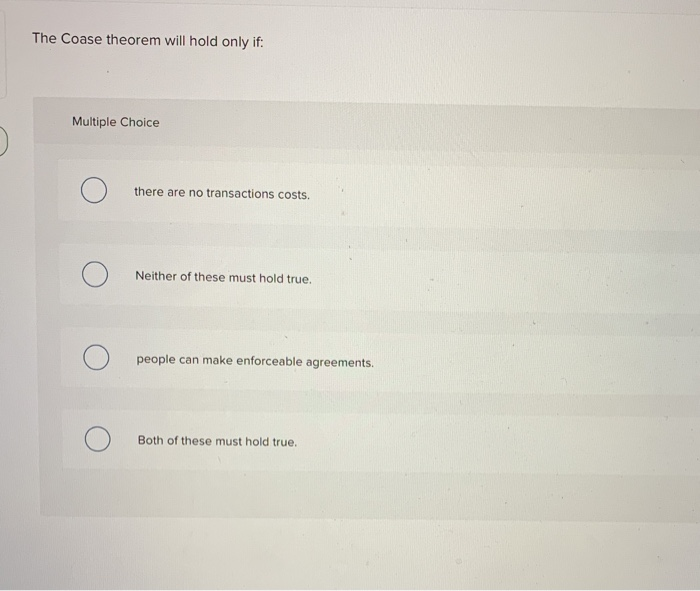
We do that in a context of households that consume public goods in addition to private goods. If property rights and liabilities for an activity are fully assigned then an e cient. Neither of these must hold true.
The Coase theorem will hold only if. If the supply curve is more inelastic than the demand curve then. Neither of these must hold true.
But again the assignment of rights will impact the distribution of income because if the most efficient owner is not initially assigned a right he or she will have to pay for it. According to the Coase Theorem under the required assumptions a efficiency can result only if producers hold the property rights. D none of the above.
The Coase theorem will hold only if. In law and economics the Coase theorem describes the economic efficiency of an economic allocation or outcome in the presence of externalities. People can make enforceable agreements.
This paper studies two cases designed by Coase analyses the effects of legal rules of external damage liability on the costs and resource allocation of the parties at issue and demonstrates that the Coase Theorem is not tenable even if. The theorem states that if trade in an externality is possible and there are sufficiently low transaction costs bargaining will lead to a Pareto efficient outcome regardless of the initial allocation of property. The Coase theorem will hold only if.
The Coase theorem will hold only if. The rents must be sufficient to support the externality - that is. No Transaction Costs.
O Both of these must hold true. The Coarse theorem will hold only if. C efficiency is not possible in the presence of an environmental externality.
When we say there are no transaction costs this refers to the cost of identifying affected parties or trading partners. It has been further argued that even the prior existence of rents would not ensure the validity of the Coase Theorem. Neither of these must hold true.
There are no transactions costs. In essence it states that private parties can solve the problem of externalities on their own if they can bargain over the allocation of resources without cost. The Coase theorem will hold only if.
Hence when there are three parties the Coase Theorem fails if and only if the core of the corresponding three player more. Voluntary participation the Coase theorem does not hold in the case of more than two players. The contracts are enforceable.
There are no transactions costs. We use this equivalence result to derive all instances in which the Coase Theorem will. The Coase theorem only works under certain assumptions.
If the producers bear a larger portion of the tax incidence than the. B an efficient outcome is possible as long as property rights are assigned. Both of these must hold true.
People can make enforceable agreements.
Solved External Benefits Accrue Multiple Choice Indirect To Chegg Com

Solved Pts Figure 74 1 The Socially Optimal Quantity Of Chegg Com

Thoughts On Teaching The Coase Theorem Theorems Social Science Teaching

Solved According To The Coase Theorem Private Negotiation Chegg Com

Solved The Coase Theorem Might Be Successful If O A There Chegg Com

Solved 4 Are The Following Statements True False Or Chegg Com
Solved The Coase Theorem Will Hold Only If Multiple Choice Chegg Com
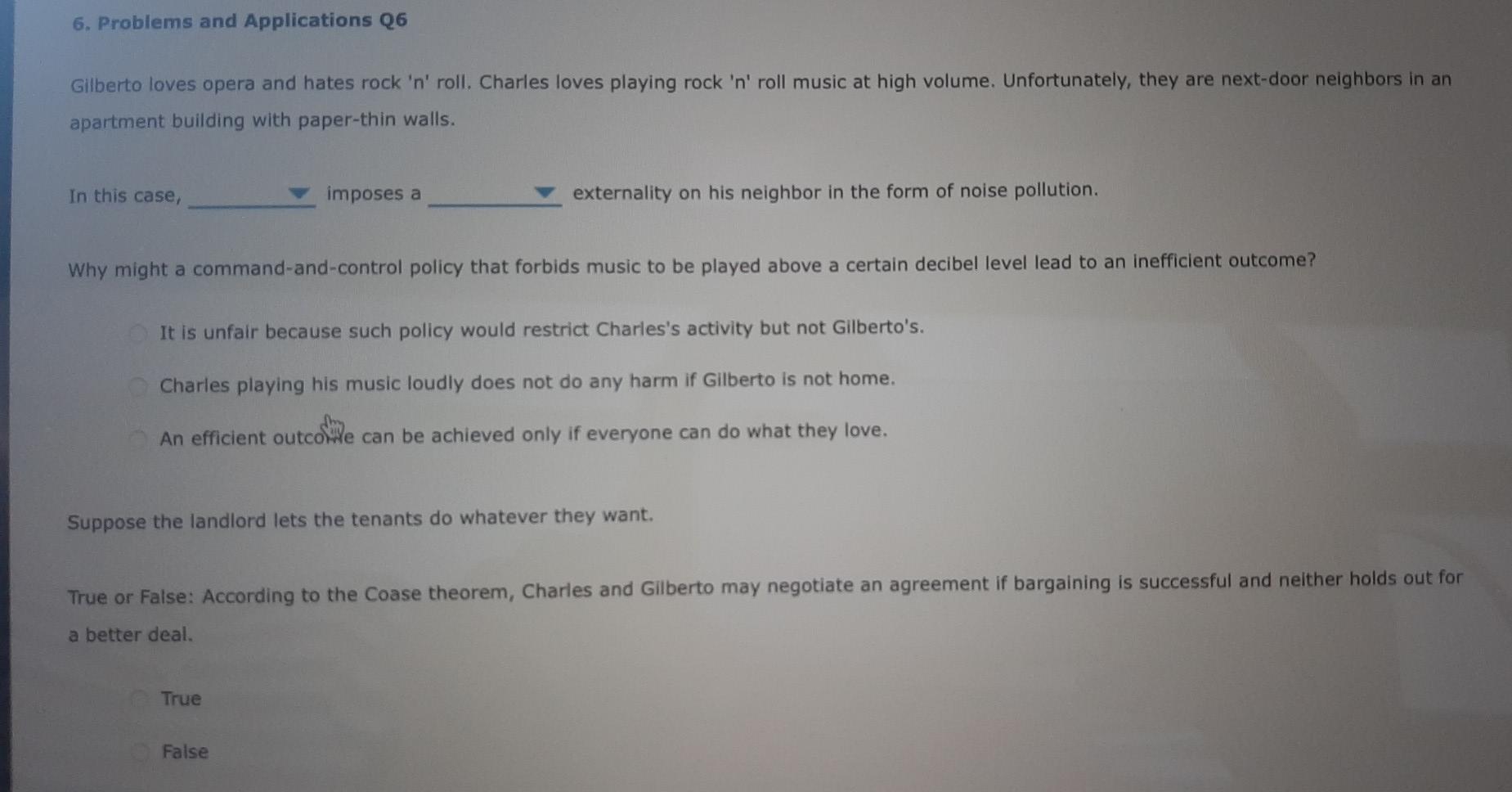
Solved 6 Problems And Applications Q6 Gilberto Loves Opera Chegg Com

Solved D Question 35 1 Pts According To The Coase Theorem Chegg Com

Solved 5 The Coase Theorem Will Apply Only If A The Courts Chegg Com

Quiz 10 Questions And Answers Quiz 10 E201 Market Failure Morrison 1 A N Is Studocu

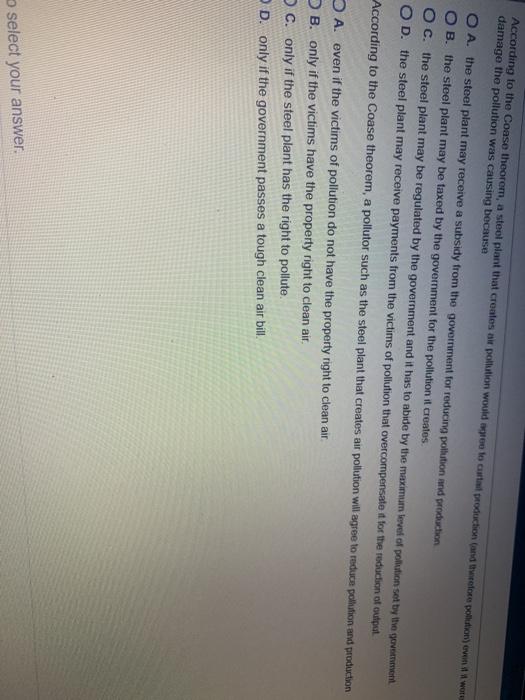
Solved According To The Coase Theorem A Pollutor Such As Chegg Com

Keynesian Economy And Multiplier Macroeconomics Macroeconomics Economics Lessons Macroeconomics Economics Notes

Solved 2 Property Rights Externalities And The Coase Chegg Com
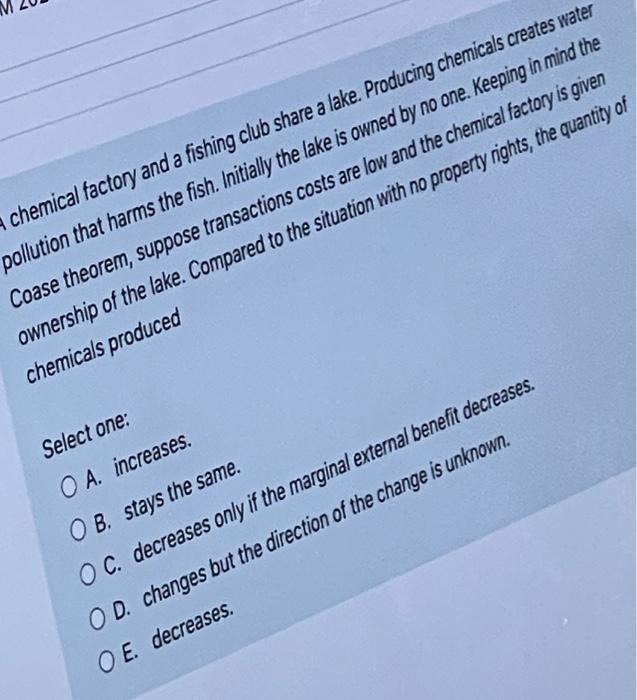
Solved A Chemical Factory And A Fishing Club Share A Lake Chegg Com

Solved According To The Coase Theorem A Steel Plant That Chegg Com
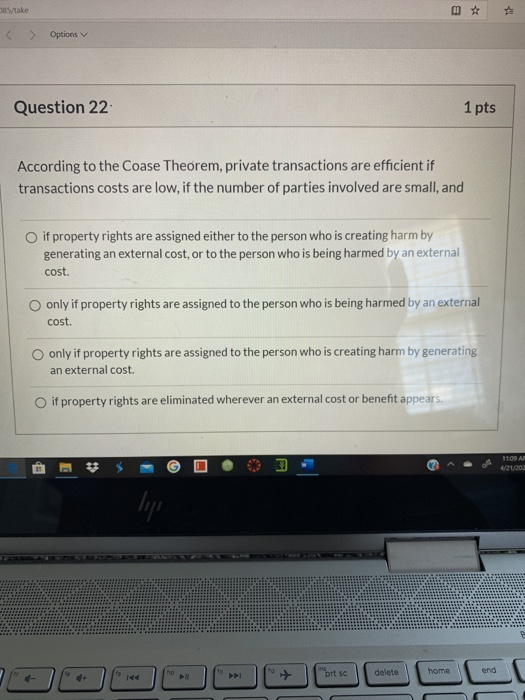
Solved Besrake Options Question 22 1 Pts According To Chegg Com

Solved Lenin S Idea That The Whole Of Society Will Have Chegg Com

Comments
Post a Comment